As a result of rapid advances in genome sequencing, the pace of discovery of new protein sequences has surpassed that of structure and function determination by orders of magnitude. This is also true for metal-binding proteins, i.e. proteins that bind one or more metal atoms necessary for their biological function.
While metal binding site geometry and composition have been extensively studied, no large scale investigation of metal-coordinating residue conservation has been pursued so far.
Our Method
In our study, we focus on conservation analysis of residues coordinating with some of the metals most commonly found in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), namely: Ca, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Na and Zn. Proteins coordinating with some of these metals have recently been analyzed based on the composition and geometry of the metal-binding site. Here, we distinguish between residues coordinating with a metal through their side-chain atoms and those coordinating through the main-chain carbonyl O. We name the former category of residues side-chain-coordinating and the latter main-chain-coordinating. Conservation is measured both as exact identity and via sequence entropy, where lower sequence entropy indicates higher conservation.
It has been shown that:
- Certain residues are preferred to others for binding to certain metals.
- The conservation of most metal-coordinating residues is correlated with residue preference in a statistically significant manner.
- There is a statistically significant difference in conservation between metal-coordinating and non-coordinating residues, with metal residues being more conserved.
- These results could be useful for providing better insight to functional importance of metal-coordinating residues, possibly aiding metal binding site prediction and design, metal-protein complex structure prediction, drug discovery, as well as model fitting to electron-density maps produced by x-ray crystallography.
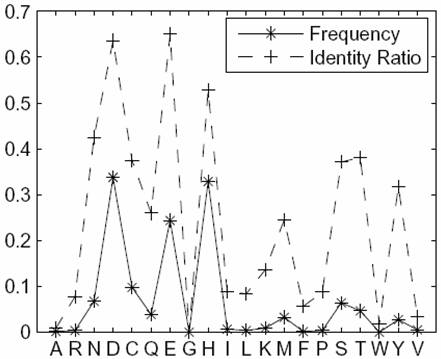 |
 |
|
Side-chain interacting residues: Identity ratio and frequency per residue type |
Mean sequence entropy of non-, side-chain and main-chain-coordinating residues interacting with different metals. Side-chain-coordinating residues show much lower sequence entropy than the other two categories, owing to higher evolutionary constraints. |
Downloads
-
Relevant Publications
I. N. Kasampalidis, I. Pitas and K. Lyroudia, "Statistical Conservation Analysis of Zinc-interacting Residues", in Proc. of Workshop on Computational Systems Biology, Tampere, Finland, pp. 41-44, June 2006.
I. N. Kasampalidis, I. Pitas and K. Lyroudia, "Conservation of Metal-coordinating Residues, Proteins: Structure, Function and Bioinformatics", in print.
Research Projects
BioPattern - Computational Intelligence for BioPattern Analysis to Support eHealth, IST
A new general strategy for measuring similarity between proteins is introduced. Our approach has its roots in computational linguistics and the related techniques for quantifying and comparing content in strings of characters.
- The pairwise comparison of proteins relies on the content regularities expected to uniquely characterize each sequence.
- These regularities are captured by n -gram based modelling techniques and in the sequel are contrasted by cross-entropy related measures.
Our Method
- In this very first attempt to fuse theoretical ideas from computational linguistics with the field of bioinformatics, we experimented with different implementations having always as ultimate goal the development of practical, computational efficient algorithms.
- The experimental analysis provides evidence for the usefulness of the new approach and motivates the further development of linguistics-related tools as a means to decipher the biological sequences.
Downloads
-
Relevant Publications
A. Bogan-Marta, M. A. Gavrielides, I. Pitas and K. Lyroudia, "A New Statistical Measure of Protein Similarity based on Language Modeling", in Proc. of IEEE Int. Workshop on Genomic Signal Processing and Statistics (GENSIPS 2005), Newport, Rode Island, SUA, 22-24 May, 2005.
A. Bogan-Marta, N. Laskaris, M. A. Gavrielides, I. Pitas and K. Lyroudia, "A Novel Efficient Protein Similarity Measure Based on N-Gram Modeling", in Proc. of IEE Second Int. Conf. on Computational Intelligence in Medicine and Healthcare (CIMED 2005), Costa da Caparica, Lisbon, Portugal, 29th June-1st July, 2005.
Research Projects
BioPattern - Computational Intelligence for BioPattern Analysis to Support eHealth, IST